Server-Side Power
We use industry-standard, server-side tools for high-quality optimization results.
Simple SVG minifier & GIF, PNG, WebP and JPEG/JPG compressor.
The online image compressor from IMGing.tools helps you to optimize and compress your images online. It reduces the file size of your images using powerful image processing algorithms, making them load faster on websites and take up less storage space, without significantly sacrificing quality.
Step 1: Upload
Drag and drop your image file onto the designated area, or click the button to select a file from your device.
Step 2: Optimize & Compress
Choose your desired optimization settings (like quality level or output format, depending on the input file type). Click the "Compress Image" button.
Step 3: Download
Preview the result/size and click the "Download" button to save the compressed image.
Our goal is to provide an easy-to-use service that helps you reduce the file size of your images without significant quality loss. This is useful for web developers, designers, bloggers, or anyone looking to make their website faster or save storage space and bandwidth.
We currently support optimization for:
We use industry-standard, server-side tools for high-quality optimization results.
Supports most common web image formats. JPG, PNG, WebP, SVG and GIF
Choose optimization levels or quality settings to suit your needs.
Easily upload your image file by dragging them onto the page.
Your files are only stored temporarily during processing and deleted immediately afterwards. We don't keep your images.
Use the tool on any device/morden-browser.
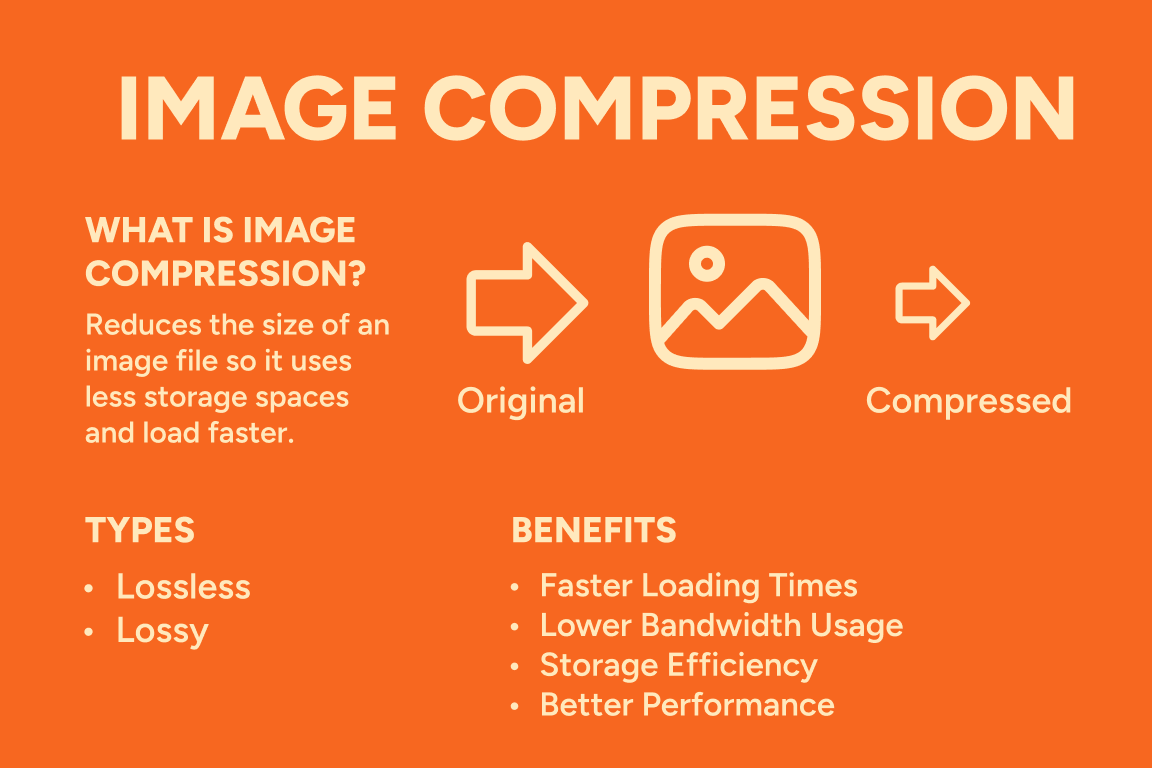
Image Compression: Making Images Faster, Smaller, and Smarter
In the age of digital content, images are everywhere—from websites and social media to apps and e-commerce platforms. While high-quality images are essential for engagement, they also come with a cost: file size. This is where image compression comes in—a powerful technique that reduces image file sizes without compromising too much on quality.
What Is Image Compression?
Image compression is the process of reducing the size of an image file so it consumes less storage space and loads faster on websites or apps. This is achieved by removing redundant or unnecessary image data.
Why Is It Important?
Types of Image Compression
There are two main types:
Best Practices for Image Compression
Choose the right file format (JPEG for photos, PNG for transparency).
Resize images to the exact dimensions needed. Try not to upload oversized images. Miniml resizing option available at IMGing.tool
Use lazy loading on websites to delay loading images until needed.
Consider next generation formats like WebP for better compression without quality loss to reduce image loading time.
Image Compression and SEO
Google favours websites that load quickly.
Compressed images help:
JPEG is the most common image format used online. It achieves small file sizes by discarding some image data, which often goes unnoticed to the human eye.
Type: Lossy
Best for: Photography and web images
Pros:
Cons:
Use It When: You are uploading photos to websites or social media and want to save space without noticeable quality loss.
PNG is known for preserving image quality. It supports transparent backgrounds, which makes it perfect for design elements.
Type: Lossless
Best for: Graphics, logos, and images needing transparency
Pros:
Cons:
Use It When: You need crisp graphics or images with transparent backgrounds, such as logos and icons.
GIFs are widely used for animated content and low-color images. However, the limited color palette makes them unsuitable for detailed visuals.
Type: Lossless (but limited to 256 colours)
Best for: Animations and simple web graphics
Pros:
Cons:
Use It When: You want to share fun animations, memes, or simple line art.
Developed by Google, WebP is a modern image file format that compresses better than JPEG and PNG. It also supports animation and transparency.
Type: Lossy or lossless
Best for: Web optimisation
Pros:
Cons:
Use It When: You want fast-loading images on websites or apps without sacrificing quality.
TIFF is a go-to format for professionals in photography, publishing, and archiving. It preserves all image data and often includes layers and metadata.
Type: Lossless or uncompressed
Best for: High-quality prints and professional editing
Pros:
Cons:
Use It When: You're editing professional-grade photos or preparing files for print.
Used by Apple devices, HEIC offers better compression than JPEG while maintaining image quality. It supports features like bursts and live photos.
Type: Lossy or Lossless
Best for: Mobile Photography
Pros:
Cons:
Use It When: You're using iPhones/iPads or want to save high-quality images without taking up too much space.
BMP is an older format that stores uncompressed image data. It's rarely used today due to its large file size and lack of features.
Type: Uncompressed or Lossless
Best for: Simple, raw image storage
Pros:
Cons:
Use It When: You're working on Windows OS specific applications that require basic image storage.
RAW formats store unprocessed image data directly from a camera sensor. Each camera brand uses its own RAW extension. For Canon: .cr2, Nikon: .nef, Sony: .arw etc.
Type: Lossless (proprietary)
Best for: Professional photography and editing
Pros:
Cons:
Use It When: You're a professional photographer or editor who needs complete control over image editing.
We're passionate about providing useful web utilities! We are actively working on adding more image processing tools and other helpful features to this website. Stay tuned for updates!
Have feedback or questions? Please contact us here